
Find physical data, electron configuration, chemical properties, aggregation states, isotope data (including decay trees) as well as some historic information. #V_"eff" = ("1 cm"^3 color(white)(l)"Po")/(9.32 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("g Po")))) × (209 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("g Po"))))/(1 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mol Po")))) × (1 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mol Po"))))/(6.022 × 10^23color(white)(l) "atoms Po")# The atomic radius and ionic radius increase as you move down the periodic table in the carbon family, while electronegativity and ionisation energy decrease. That is, the atom fills only 52.36 % of the unit cell.Įxperimentally, the effective volume of an atom is The atom occupies the whole cube, so its effective volume is We see that there is 1 atom per unit cell ( #1/8 "atom"# at each corner) and that the edge length of the cell ( #a#) is twice the atomic radius ( #r#). In the case of Carbon There are cool facts about Carbon that most dont know about. Let's calculate the atomic radius of polonium, which has molar mass = 209 g/mol, density = #"9.32 g/cm"^3#, and exists in a simple cubic unit cell. Note: Learn more about the atomic radius here.
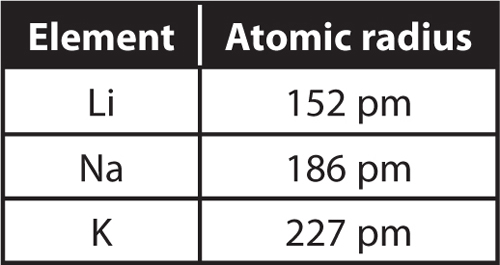
For a metal, you need the density, the molar mass, and the crystal structure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
